算法提升——数组和链表篇
最后更新时间:
数组和链表
基本概念
基本存储结构:顺序存储、链式存储
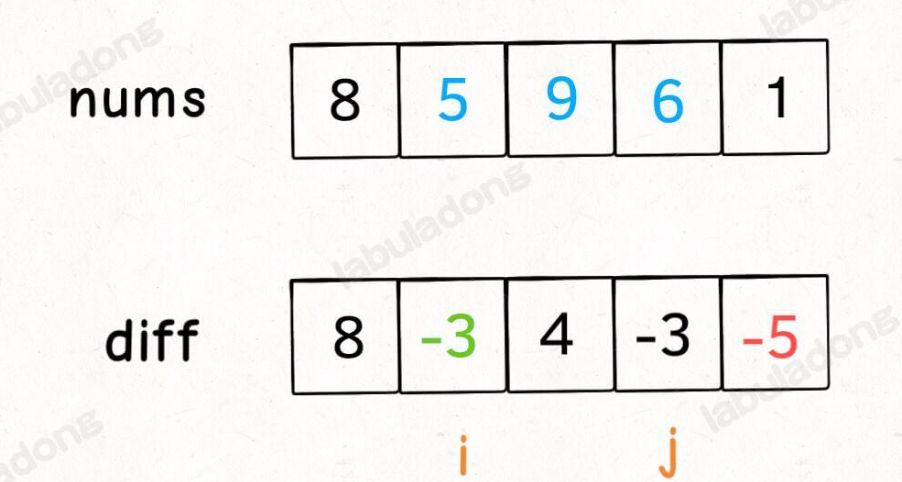
数组
「随机访问特性的成因」:每个元素的内存地址可以直接推算出来。
- 数组中的第一个元素地址已知
- 每个元素占有的空间确定
- 数组之间紧凑存储(链表就不是这样,其元素之间内存非连续分配)
紧凑特性带来的代价:
- 增删操作需要搬移整体元素
- 扩容困难,只能重新申请大数组并整个复制旧数组中的元素
「ArrayList 的原理分析」
- 扩容/缩容机制实现:
resize(int newCap)

检查数组是否越界:
checkElementIndex(int index)
细节:
position索引实际定义的元素与元素之间的间隙索引数组尾部添加元素:
addLast()写逻辑代码之前先作前置条件限制

数组任意位置添加元素
add(int index, E element)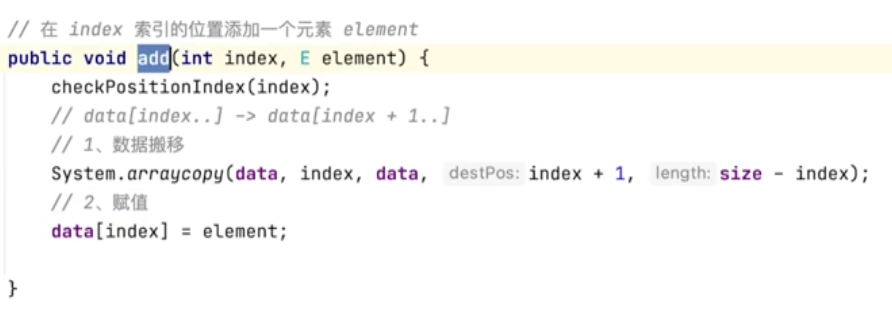
先做数组搬移,再插入元素,
size++
链表
底层原理:利用 next 指针来指向下一元素的内存地址
非紧凑特性带来的代价:
- 新增元素都需要为其维护指针的地址空间
「LinkList 的原理分析」
链表结构(双链表)

head 和 tail 的占位符作用:事先创建两个空节点,避免删除和新增首尾节点时出现错误

添加首部元素
addFirst(E e)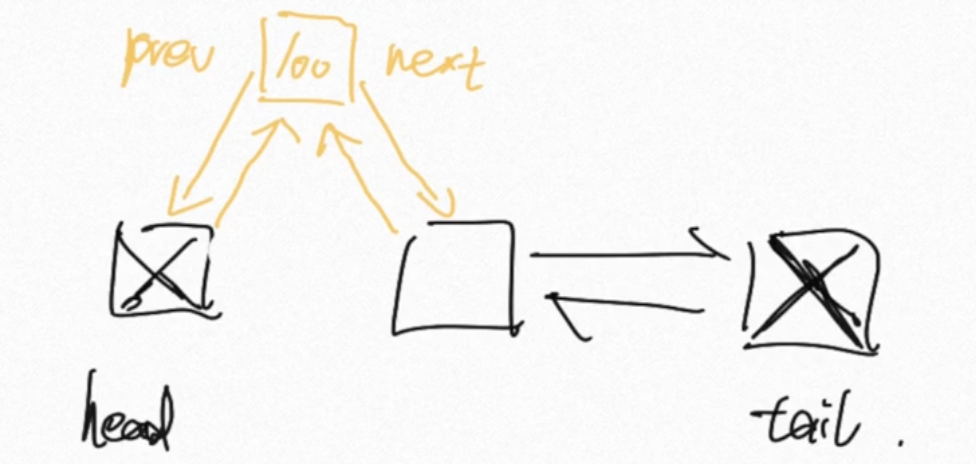

删除首部元素
removeFirst()将指向最后一个元素的指针
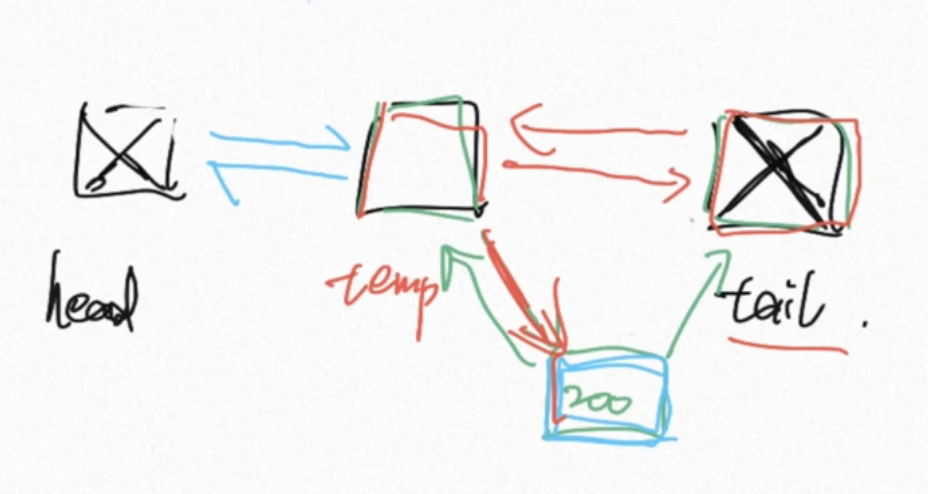
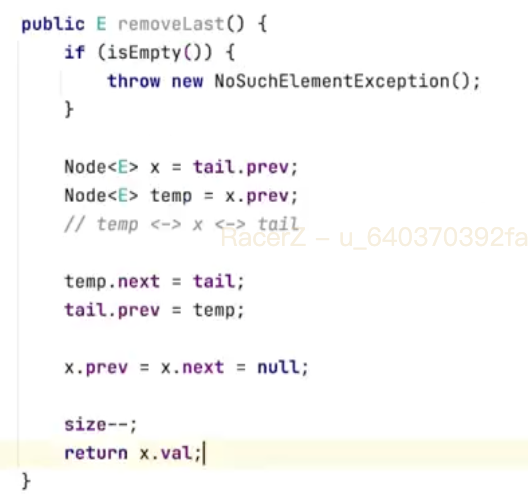
对于带有 index 指定节点的操作,需要先遍历定位节点
细节:对于 index,判断一下其在整个链表中的指向位置,可以对遍历效率做一些优化
add(int index, E element)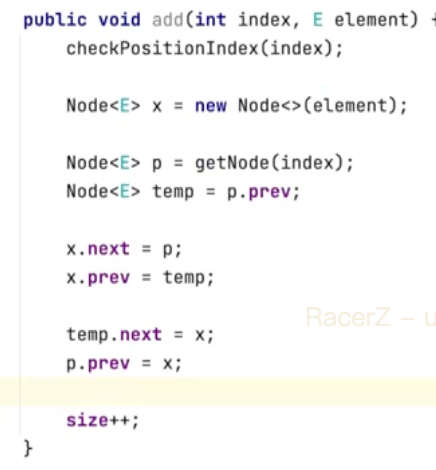
remove(int index) 同理

单链表技巧套路
「虚拟节点 dummy」的使用
合并两个有序链表 => leetcode-21 合并两个有序链表
这里为了简化指针的处理,可以添加一个「虚拟节点」,作为合成链表的头部起点(最后返回的时候从第二个节点返回即可)
当你需要创造一条新链表的时候,可以使用虚拟头结点「简化边界」情况的处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p1 = list1, p2 = list2;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1), p = dummy;
while(p1!=null && p2!=null) {
if (p1.val > p2.val) {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
} else {
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (p1 != null) {
p.next = p1;
}
if (p2 != null) {
p.next = p2;
}
return dummy.next;
}进阶:
利用的方法是 Sieve of Eratosthenes 素数筛
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public int countPrimes(int n) {
boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[n];
Arrays.fill(isPrime, true);
// 优化处理
for (int i = 2; i * i < n; i++) {
if (isPrime[i] == true) {
// 优化处理 i 整数倍 考虑 2 时的 2x5 和 5 时的 5x2
for(int j = i * i; j < n; j += i) {
isPrime[j] = false;
}
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (isPrime[i] == true) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}这里的优化部分都是看的平方项,可以参考如下:可以看到前后对称的
1
2
3
4
512 = 2 × 6
12 = 3 × 4
12 = sqrt(12) × sqrt(12)
12 = 4 × 3
12 = 6 × 2🚩回到正题:leetcode-264 丑数 II
这道题结合素数筛的思路,可以直接定位 2 / 3 / 5 的倍数. 另外,结合合并链表的思想,我们实际上就是对三个链表进行去重合并,然后返回给定位置值即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
int p2 = 1, p3 = 1, p5 = 1;
int[] ugly = new int[n + 1];
// 1 也是丑数
int product2 = 1, product3 = 1, product5 = 1;
int p = 1;
while (p <= n) {
int min = Math.min(product2, Math.min(product3, product5));
ugly[p] = min;
p++;
if (product2 == min) {
// 这里应该作了优化,并非直接顺着各自链表,方便排除重复项;同时
// 取最小值避免遗漏
product2 = 2 * ugly[p2];
p2++;
}
if (product3 == min) {
product3 = 3 * ugly[p3];
p3++;
}
if (product5 == min) {
product5 = 5 * ugly[p5];
p5++;
}
}
return ugly[n];
}单链表的分解 leetcode-86 分隔链表
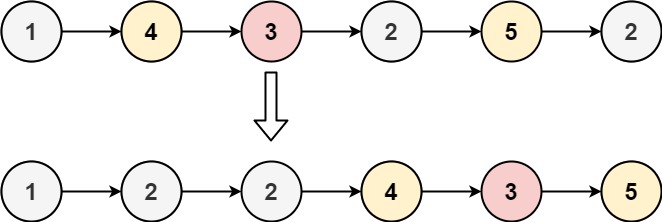
一张图可以看到,实际上这是一个分解再合并链表的过程:先分解成小于 x 和 大于 x 的两组链表,然后合并即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode dummy1 = new ListNode(-1), p1 = dummy1 ;
ListNode dummy2 = new ListNode(-1), p2 = dummy2;
ListNode p = head, temp;
while(p != null) {
if (p.val < x) {
p1.next = p;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p2.next = p;
p2 = p2.next;
}
// 注意原链表的 next
temp = p.next;
p.next = null;
p = temp;
}
p1.next = dummy2.next;
return dummy1.next;
}进阶:leetcode-1836 从未排序的链表中移除重复元素
这道题本质蕴含了链表分解的思路,我们遍历两次链表,第一次记录哪些值出现重复,然后第二次将无重复的节点分解出来
当然这里记录重复项用的是 HashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28public ListNode deleteDuplicatesUnsorted(ListNode head) {
ListNode p = head;
// 先遍历一遍链表,记录每个值出现的次数
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap();
while (p != null) {
map.put(p.val, map.getOrDefault(p.val, 0) + 1);
p = p.next;
}
// 虚拟头结点(哨兵节点),存放结果链表
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
// 再遍历一遍节点,把重复出现的节点剔除
p = dummy;
while(p != null) {
// unique 指针负责寻找不重复的节点
ListNode unique = p.next;
while (unique != null && map.get(unique.val) > 1) { // 跳过重复节点,直到找到不重复的节点
unique = unique.next;
}
// 跳过重复节点,直到找到不重复的节点
p.next = unique;
// p 前进,继续寻找不重复节点
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}-
这题看起来很像合并有序链表的思路,但是区别在于数组元素在物理上是连续排布的,直接按照合并链表的逻辑,将导致原数组元素被覆盖。但是这里给的第一个数组后面为空 0 元素,那么说明我们可以从大到小排布,这样即使前面的元素被覆盖了,但是也已经被使用过
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m - 1;
int j = n - 1;
int p = nums1.length - 1;
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (nums1[i] > nums2[j]) {
nums1[p] = nums1[i];
i--;
p--;
} else {
nums1[p] = nums2[j];
j--;
p--;
}
}
while(j >= 0) {
nums1[p] = nums2[j];
j--;
p--;
}
} -
这里平方操作将导致所有的负数都变为正数,那么结合前面题的思路,我们可以将双指针放在两端,由非递减属性可知,平方后的元素肯定是两边大,中间小。双指针相向遍历判断大小然后倒着放在新数组中即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
int[] res = new int[n];
int p = n - 1;
while(i <= j) {
if (Math.abs(nums[i]) > Math.abs(nums[j])) {
res[p] = nums[i] * nums[i];
p--;
i++;
} else {
res[p] = nums[j] * nums[j];
p--;
j--;
}
}
return res;
} -
这里二次函数要联想到它的抛物线,通过开口方向和对称轴位置来判断两侧的数值大小走向。我们仍然可以沿用双指针相向扫描的思路,只不过判断一下是先合并大的值还是小的值(对于开口向上的抛物线,越靠近抛物线值会越小,因此采用递减排列;对于开口向下的抛物线,越靠近抛物线值会越大,因此采用递增排列)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38public int[] sortTransformedArray(int[] nums, int a, int b, int c) {
int n = nums.length;
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
int p = a > 0 ? n - 1: 0;
int[] res = new int[n];
while(i <= j) {
int v1 = f(nums[i], a, b, c);
int v2 = f(nums[j], a, b, c);
if (a > 0) {
if (v1 > v2) {
res[p] = v1;
p--;
i++;
} else {
res[p] = v2;
p--;
j--;
}
} else {
if (v1 > v2) {
res[p] = v2;
p++;
j--;
} else {
res[p] = v1;
p++;
i++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private int f(int x, int a, int b, int c) {
return a*x*x + b*x + c;
} -
这题看起来就 split reverse and join 即可,但是里面存在空格问题不好处理。如果用双指针操作也是可以的,我可以将整个字符串先进行反转,再对字符串中的单词进行反转,当然字符串格式需要事先调整好空格数量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c != ' ') {
sb.append(c);
} else if (!sb.isEmpty() && sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) != ' ')
// 单词之间仅保留一个空格
sb.append(' ');
}
// 考虑最后一个空格
if (sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) == ' ') {
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
// 转换为字符数组操作单个字符
char[] str = sb.toString().toCharArray();
int n = str.length;
reversed(str, 0, n - 1);
for(int i = 0; i < str.length;) {
// 扫描单词
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
// 识别到单词
if (j + 1 == n || str[j + 1] == ' ' ) {
reversed(str, i, j);
i = j + 2;
break;
}
}
}
return new String(str);
}
private void reversed(char[] arr, int i, int j) {
while (i < j) {
char tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
} 🚩合并 k 个有序链表 leetcode-23 合并K个升序链表
这里为了每次能快速从 k 个节点中找到最小的放到合并链表上,引入「优先级队列(二叉堆)」结构
优先级队列的实现就是基于二叉堆的「上浮」和「下沉」操作来完成的;
时间复杂度:优先队列
pq中的元素个数最多是k,所以一次poll或者add方法的时间复杂度是O(logk);所有的链表节点都会被加入和弹出pq,所以算法整体的时间复杂度是O(Nlogk),其中k是链表的条数,N是这些链表的节点总数
Java 提供了实现类 PriorityQueue

1 | |
-
可以把每一行或每一列看作一个链表,那么问题就变成了合并 k 个生序问题了.
注意细节在于需要记录每个元素的位置,方便后面添加对应行的下一个元素
数据结构可设计为
(value, i, j)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int min = -1;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> (a[0] - b[0]));
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
// 将指定的元素插入队列。如果队列已满,则返回false
pq.offer(new int[] {matrix[i][0], i, 0});
}
while (!pq.isEmpty() && k > 0) {
int[] element = pq.poll();
min = element[0];
k--;
int index = element[1], j = element[2];
if ((j+1) < matrix.length) {
pq.add(new int[] {matrix[index][j+1], index, j+1});
}
}
return min;
} -
同样可以看出来合并的意思在里头,如何构造待合并序列呢?

妙哉,直接两两配对即可,而且每个链表我也可以保证是有序的
当然要保留一个索引号来记录下一个放入队列的索引
数据结构设计为
(value1, value2, index)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> ((a[0] + a[1]) - (b[0] + b[1]))
);
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
pq.offer(new int[] {nums1[i], nums2[0], 0});
}
ArrayList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
while(!pq.isEmpty() && k > 0) {
int[] element = pq.poll();
int j = element[2];
k--;
if (j + 1 < nums2.length) {
pq.offer(new int[]{element[0], nums2[j+1], j+1});
}
ArrayList pair = new ArrayList();
pair.add(element[0]);
pair.add(element[1]);
res.add(pair);
}
return res;
}
单链表的倒数第 k 个节点(仅给出头节点)
传统方法:从头节点遍历,得到链表长度 n ,再定位至 n-k+1 位置得到答案
如何通过仅遍历一次链表就能定位到倒数第 k 个节点?
利用双指针配合来定位:首先 p1 走 k 步到达某点,再走 n-k 步即可到达结尾空指针
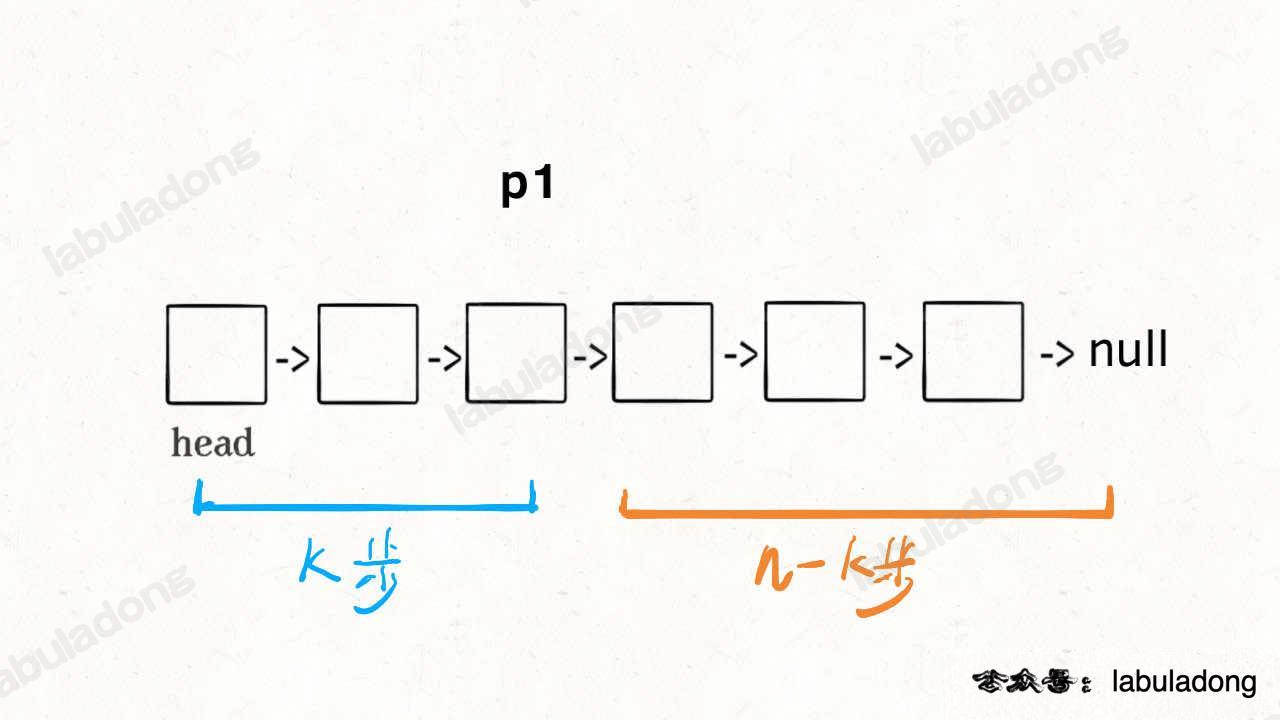
这时我们可以再用另一指针 p2,当 p1 到达第 k 个节点时,p2 同步出发直至 p1 到达空指针处
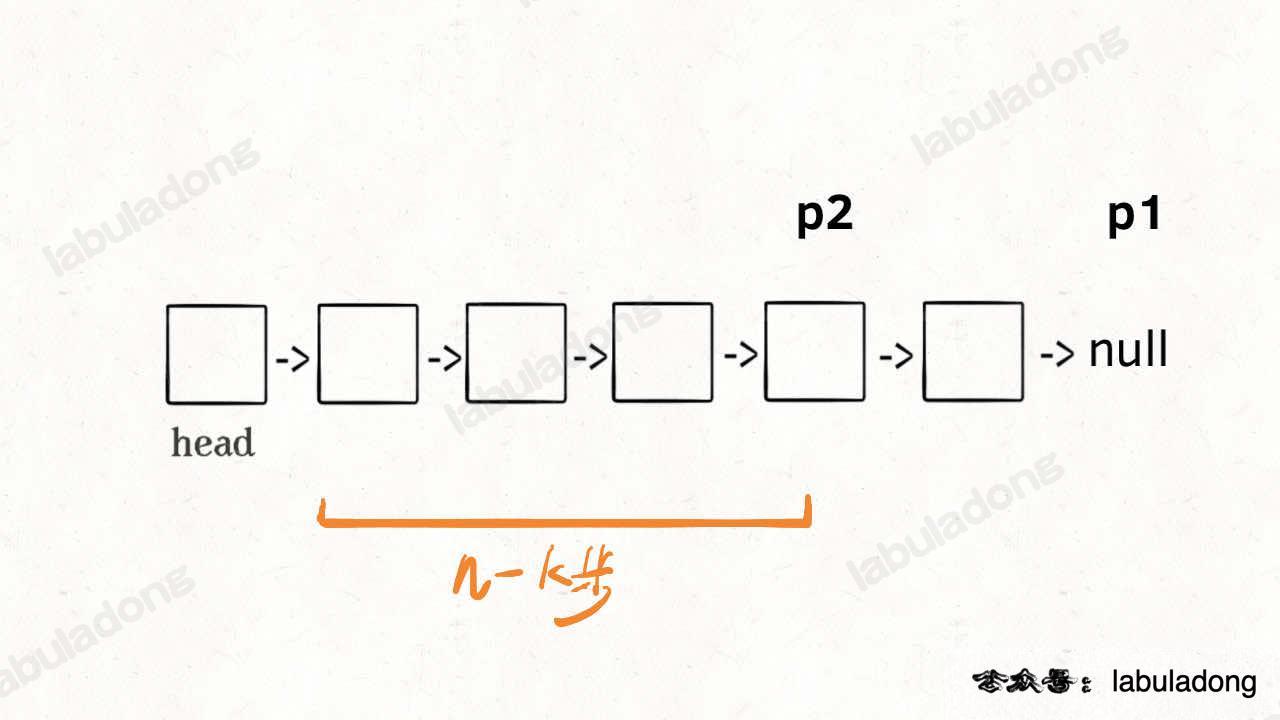
应用:
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
return realGetFromEnd(dummy, k);
}
private ListNode realGetFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode p1 = head, p2 = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
while(p1 != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p2;
} -
这里的思路就是找到倒数第 N+1 个节点,也就是目标节点的前驱。通过设置虚拟节点来避免删除第一个节点时产生的越界问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prior = returnFromEnd(dummy, n+1); // 倒数第 n+1 个节点
ListNode Temp = prior.next;
prior.next = Temp.next;
Temp.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode returnFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode p1, p2;
p1 = head; p2 = head;
for(int i=0; i < n; i++) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
while(p1 != null) {
p2 = p2.next;
p1 = p1.next;
}
return p2;
}
单链表的中点
同样在仅知链表头节点的情况下传统方法先遍历获得长度 n ,然后再定位到 n/2 的节点上
一遍遍历的思路本质上和之前倒数第 k 个节点一样,这里取名「快慢指针」更合适些,即慢指针每移动一步,快指针就移动两步,直至后者到达结尾处
应用
1 | |
如果链表长度为偶数,也就是说中点有两个的时候,我们这个解法返回的节点是靠后的那个节点
判断链表是否包含环
这个直接基于前面中点问题稍作修改即可,也就是在结果判定上,如果快指针遇到空指针就无环;而如果快指针遇到了满指针就说明有环
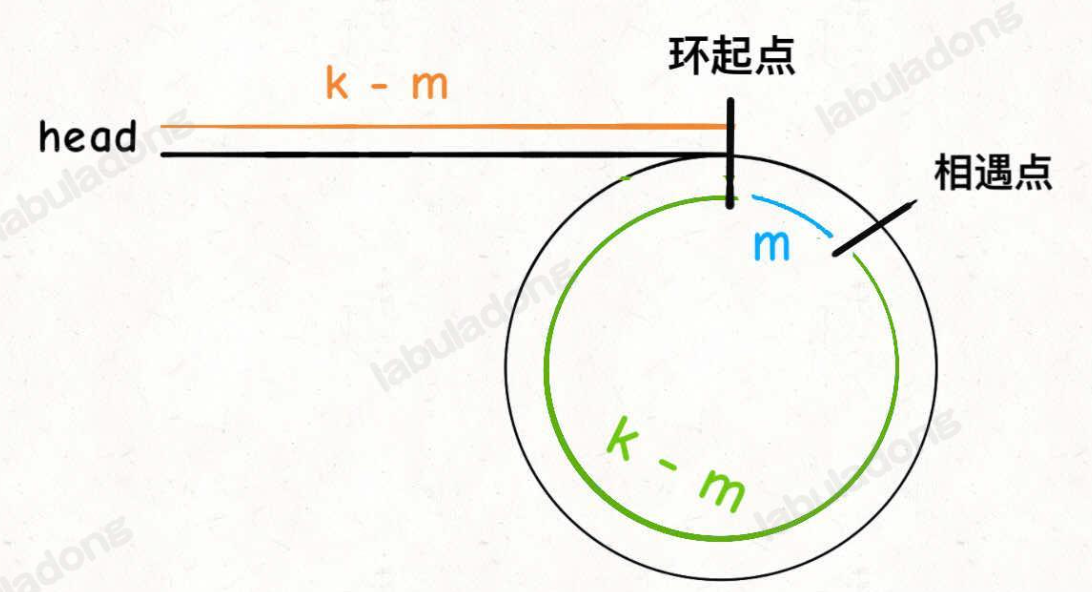
进一步,如果链表中含有环,怎么计算环的起点?
利用的还是快指针是慢指针步数 2 倍的性质:
只要我们把快慢指针中的任一个重新指向
head,然后两个指针同速前进,k - m步后一定会相遇,相遇之处就是环的起点了
应用:
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1 | |
两个链表是否相交
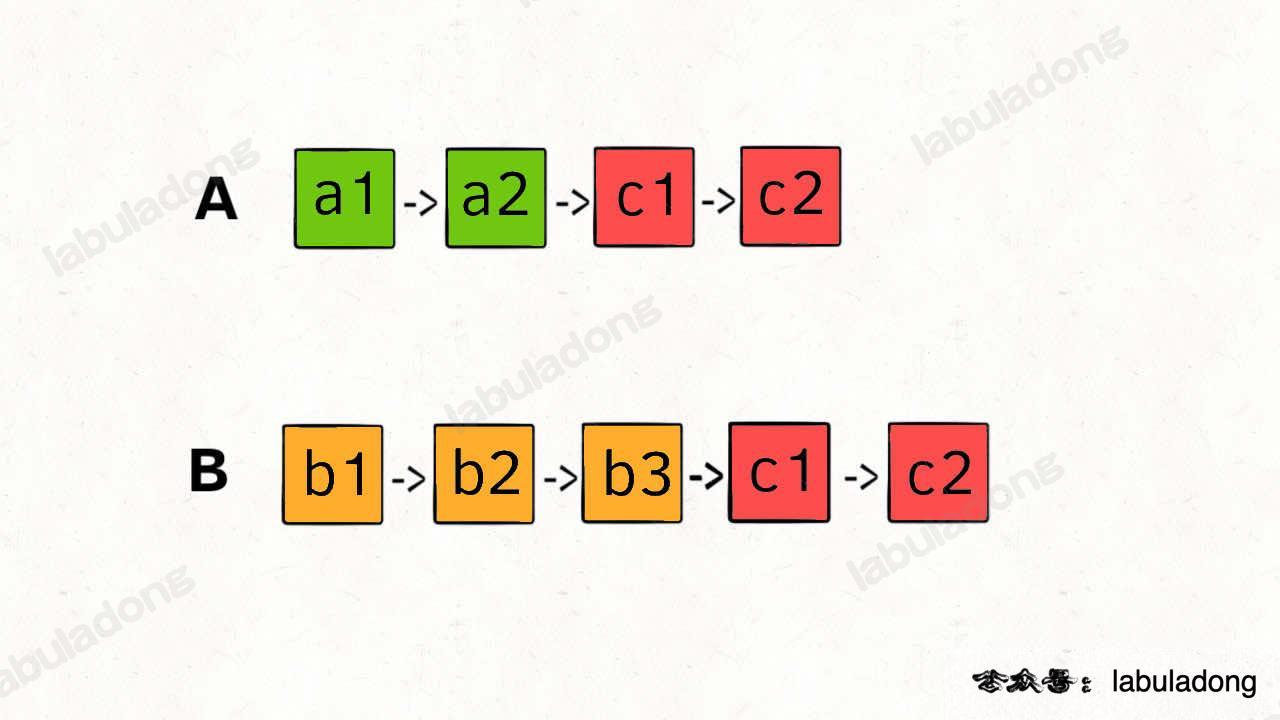
这里主要需要解决的问题在于两条链表长度可能不同,无法通过分别遍历的方式使得两个链表指针同时指向相交节点
一个巧妙思路就是,「逻辑上」将两个链表连接在一起,即两边指针均遍历完自己的节点后继续遍历对方的节点
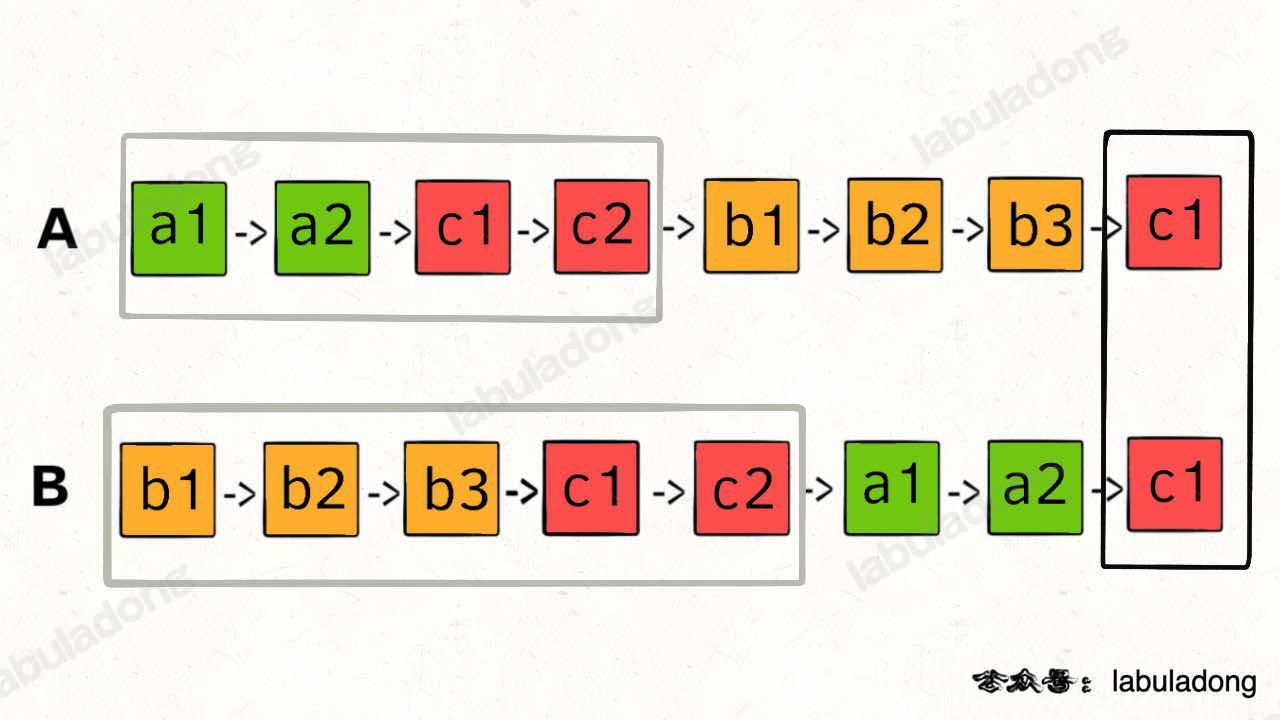
如果两者无相交,即 c1 节点对应空指针
1 | |
数组双指针技巧
在数组中,指针的含义其实就是元素的索引。这里的双指针包含快慢指针和左右指针两种用法
- 「快慢指针」技巧
原地修改数组
这里利用慢指针作为修改指针,快指针作为探路指针。如果快指针遇见非重复项,就告诉慢指针前进一步并修改元素
这样,就保证了
nums[0..slow]都是无重复的元素,当fast指针遍历完整个数组nums后,nums[0..slow]就是整个数组去重之后的结果
1 | |
应用:
-
本质是一样的,唯一区别在于数组赋值操作变成操作指针而已
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null ){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null) {
if (fast.val != slow.val) {
slow.next = fast;
slow = slow.next;
}
fast = fast.next;
}
// 考虑最后出现重复的情况
slow.next = null;
return head;
}
进阶:
这里不仅让你找出重复元素,而且还要全部除去
双指针思路:
1 | |
还有一种递归解法:
1 | |
原地删除数组
我们想把数组
nums中所有值为val的元素原地删除思路:如果
fast遇到值为val的元素,则直接跳过,否则就赋值给slow指针,并让slow前进一步应用:
-
这里注意和去重操作时的区别在于满指针增加的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int slow = 0, fast = 0;
while (fast != nums.length) {
if (nums[fast] != val) {
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
return slow;
} -
这里的思路其实就是原地删除的思路,删掉所有的 0 元素,然后最后在末尾补 0 即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int fast = 0, slow = 0;
while(fast != nums.length) {
if (nums[fast] != 0) {
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
while(slow != nums.length) {
nums[slow] = 0;
slow++;
}
}
-
TODO:滑动窗口算法
- 「左右指针」技巧
二分查找
查找框架
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = ...;
while(...) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
...
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = ...
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = ...
}
}
return ...;
}三点细节:
...部分是需要仔细审查的地方mid = left + (right - left) / 2与(left + right) / 2本质上是一样的,但前者可以有效解决 left 和 right 太大导致的整数溢出问题- 所有 else if 写清楚
缺陷:

典型例题:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}寻找左侧边界的二分搜索
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16int left_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length; // 注意
while (left < right) { // 注意
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid; // 注意
}
}
return left;
}首先右侧边界改变,因此搜索区间为左闭右开区间;其次,由于是要找左侧边界,因此当找到符合目标值时不是直接返回,而是进一步压缩右侧边界,不断向左侧边界逼近
如果要判断 left 索引是否是目标值,则:
注意要先判断下标是否越界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7while (left < right) {
//...
}
// 此时 target 比所有数都大,返回 -1
if (left == nums.length) return -1;
// 判断一下 nums[left] 是不是 target
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;寻找右侧边界的二分查找
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15int right_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
left = mid + 1; // 注意
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
}
}
return left - 1; // 注意
}这里还是采用左闭右开的搜索区间,注意:
当找到一个目标值时,左侧区间向右边界靠拢
因为每次对 left 更新都是
left = mid + 1,就是说 while 循环结束时,nums[left]一定不等于target了,而nums[left-1]可能是target(根据更新操作来看)。对于返回索引是否为目标值的判断,这里考虑的是下界可能会越界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8while (left < right) {
// ...
}
// 判断 target 是否存在于 nums 中
// 此时 left - 1 索引越界
if (left - 1 < 0) return -1;
// 判断一下 nums[left] 是不是 target
return nums[left - 1] == target ? (left - 1) : -1;
左闭右闭形式模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55int binary_search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if(nums[mid] == target) {
// 直接返回
return mid;
}
}
// 直接返回
return -1;
}
int left_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if (nums[mid] == target) {
// 别返回,锁定左侧边界
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// 判断 target 是否存在于 nums 中
// 此时 target 比所有数都大,返回 -1
if (left == nums.length) return -1;
// 判断一下 nums[left] 是不是 target
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}
int right_bound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if (nums[mid] == target) {
// 别返回,锁定右侧边界
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 此时 left - 1 索引越界
if (left - 1 < 0) return -1;
// 判断一下 nums[left] 是不是 target
return nums[left - 1] == target ? (left - 1) : -1;
}应用
两数之和
本质思想和二分查找一样的,通过移动左右指针来调节 sum 向目标值靠拢
应用:
-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int left = 0, right = numbers.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = numbers[left] + numbers[right];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[] {left+1, right+1};
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else if (sum > target) {
right--;
}
}
return new int[] {-1, -1};
} -
这道题比较坑的是需要先排序,但是就会丢失原来元素的下标信息,因此需要额外的数据结构来保存下标信息
二分法对于这道题不是最优解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27static class tuple {
int val;
int index;
}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
tuple[] temp = new tuple[nums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
temp[i] = new tuple();
temp[i].val = nums[i];
temp[i].index = i;
}
Arrays.sort(temp, (x, y) -> (x.val - y.val));
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = temp[left].val + temp[right].val;
if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else if (sum > target) {
right--;
} else if (sum == target) {
return new int[] {temp[left].index, temp[right].index};
}
}
return new int[] {};
}
-
反转数组
同理左右指针相向而行,边走边交换值
应用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
char temp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
}回文串判断
应用:
-
这里算法核心在于从中心向两端扩散的双指针技巧
这里的“中心”我们可以任意选择,左右指针从它开始向两边移动。同时,考虑“中心”为奇数点和偶数点的情况
首先是中心展开
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8private String Palindrome(String s, int l, int r) {
while(l >= 0 && r < s.length() && s.charAt(l) == s.charAt(r)) {
l--;
r++;
}
return s.substring(l + 1, r);
}然后就是遍历每一个“中心”,寻找最长回文串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
String res = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 奇数回文串
String res1 = Palindrome(s, i, i);
// 偶数回文串
String res2 = Palindrome(s, i, i + 1);
res = res.length() > res1.length() ? res : res1;
res = res.length() > res2.length() ? res : res2;
}
return res;
}
-
前缀和
前缀和技巧适用于快速、频繁地计算一个索引区间内的元素之和
-
传统我们统计一个区间内元素和就是通过遍历一遍然后累计求和,时间复杂度为
O(N),如果多次调用则很费时间。一个技巧就是提前求和前缀和:维护一个前缀和数组preSum出来,preSum[i]记录nums[0..i-1]的累加和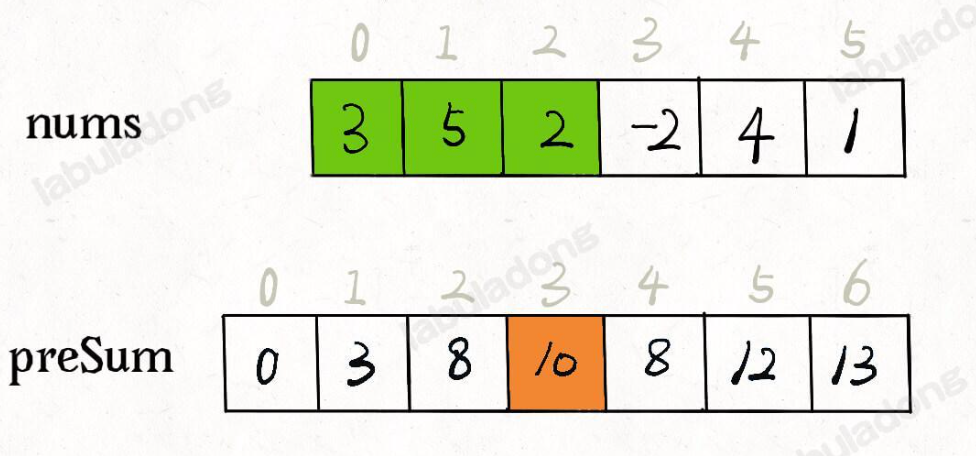
要求某个区间和时,只需要作差即可,时间复杂度降为
O(1)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class NumArray {
private int[] preNum;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
preNum = new int[nums.length + 1];
preNum[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length + 1; i++) {
preNum[i] = preNum[i-1] + nums[i-1];
}
}
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
return preNum[right + 1] - preNum[left];
}
}直接利用前缀和即可,考虑边界情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37class Solution {
int[] preNums;
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
preNums = new int[nums.length + 1];
preNums[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < preNums.length; i++) {
preNums[i] = preNums[i-1] + nums[i-1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int leftSum, rightSum;
if (i == 0) {
leftSum = 0;
} else {
leftSum = getSum(0, i - 1);
}
if (i == nums.length - 1) {
rightSum = 0;
} else {
rightSum = getSum(i+1, nums.length - 1);
}
if (leftSum == rightSum) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int getSum(int i, int j) {
return preNums[j+1] - preNums[i];
}
} 二维矩阵中的前缀和 leetcode-304 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变
观察下图可知,一个矩阵和可由多个大的矩阵组合运算得到,而这几个大矩阵的共同点都是以原点作为起点
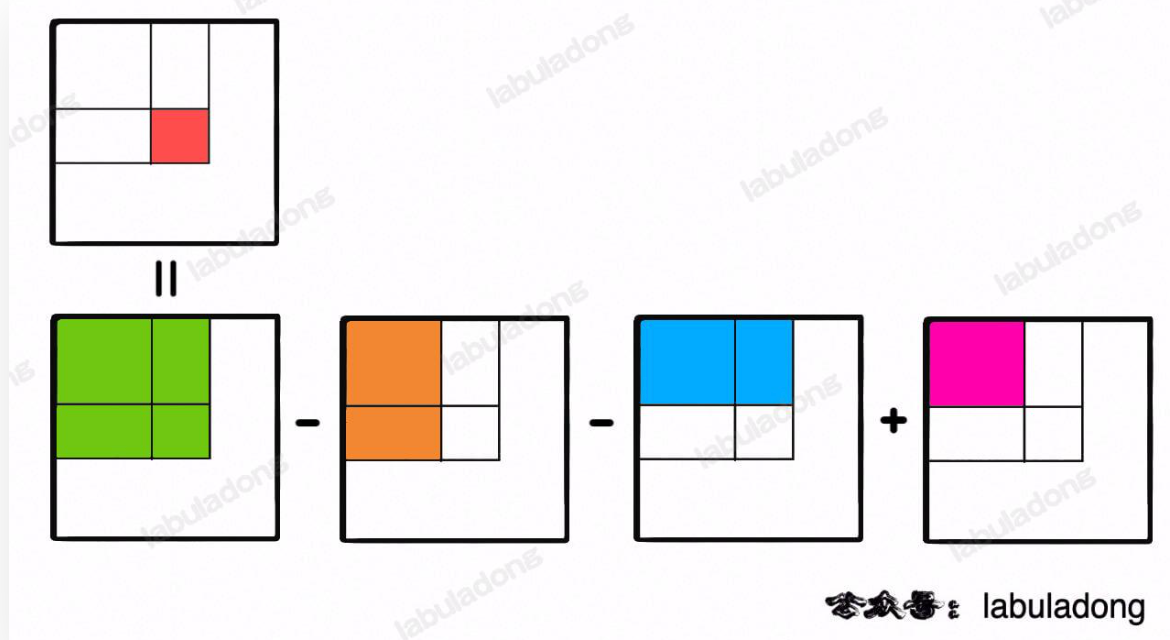
那么我们完全可以计算所有以原点为起点的前缀和矩阵,用的时候将他们组合运算即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23class NumMatrix {
private int[][] preMatrix;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
preMatrix = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
if (m == 0 && n == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
preMatrix[i][j] = preMatrix[i-1][j] + preMatrix[i][j-1] + matrix[i-1][j-1] - preMatrix[i-1][j-1];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return preMatrix[row2+1][col2+1] - preMatrix[row2+1][col1] - preMatrix[row1][col2+1] + preMatrix[row1][col1];
}
}-
思路基本和上题一样,需要注意下标越界问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36class Solution {
int[][] preMatrix;
public int[][] matrixBlockSum(int[][] mat, int k) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
if (m == 0 && n == 0) return null;
preMatrix = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
preMatrix[i][j] = preMatrix[i-1][j] + preMatrix[i][j-1] + mat[i-1][j-1] - preMatrix[i-1][j-1];
}
}
int[][] answer = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 防止数组越界
int row1 = Math.max(i-k, 0);
int col1 = Math.max(j-k, 0);
int row2 = Math.min(i+k, m-1);
int col2 = Math.min(j+k, n-1);
answer[i][j] = sum(row1, col1, row2, col2);
}
}
return answer;
}
private int sum(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return preMatrix[row2+1][col2+1] - preMatrix[row1][col2+1] - preMatrix[row2+1][col1] + preMatrix[row1][col1];
}
} 前缀积
这里的思想和前缀和数组很类似,通过构造前缀积和后缀积,两个相乘就是除自身以外数组的乘积
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int length = nums.length;
int[] preix = new int[length];
preix[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
preix[i] = preix[i-1] * nums[i];
}
int[] suffix = new int[length];
suffix[length - 1] = nums[length - 1];
for (int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffix[i] = suffix[i+1] * nums[i];
}
int[] answer = new int[length];
// 边界情况
answer[0] = suffix[1];
answer[length - 1] = preix[length - 2];
for (int i = 1; i < length - 1; i++) {
answer[i] = preix[i-1] * suffix[i+1];
}
return answer;
}前缀和 + 哈希表
前面都是给定索引区间去求前缀和,那么给定前缀和如何去求解索引区间?
这里就要借助哈希表来维护每一个前缀和的索引
我们已知
target = preSum[j] - preSum[i],也就是说只要哈希表中维护了索引的映射关系,那么遍历 i 或 j (这里以 j 为例)preSum[i] = target - preSum[j]只要每次去判断是否存在 i 的映射即可这题的解法十分巧妙,数量相同可以转为和为0的最长子数组,也就是将 0 元素转为值为 -1 。这样就可以用前缀和的思路,配合哈希表记录前缀和的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < len + 1; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + (nums[i-1] == 0 ? -1 : 1);
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length; i++) {
if (!map.containsKey(prefix[i])) {
map.put(prefix[i], i);
} else {
// 说明出现了和 0 的子数组
res = Math.max(res, i - map.get(prefix[i]));
}
}
return res;
}
}求解条件可以转换为:寻找
i, j使得(preSum[i] - preSum[j]) % k == 0且i - j >= 2也就是 preSum[i] 和 preSum[j] 模 k 同余
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public boolean checkSubarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int len = nums.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prefix.length; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1];
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length; i++) {
if (!map.containsKey(prefix[i] % k)) {
map.put(prefix[i] % k, i);
} else if ((i - map.get(prefix[i] % k)) >= 2) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}这道题关键是我需要知道对于当前的 prefix,它的 need = prefix - k
是否存在且存在多少个。因此区别于前面几题,这题需要提前维护一个记录 need 值和出现个数的 map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int len = nums.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
count.put(0, 1);
int res = 0; // 总子数组个数
for (int i = 1; i < prefix.length; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1];
// 对于该前缀和,还需多少来满足和为 k
int need = prefix[i] - k;
if (count.containsKey(need)) {
res += count.get(need);
}
if (!count.containsKey(prefix[i])) {
count.put(prefix[i], 1);
} else {
count.put(prefix[i], count.get(prefix[i]) + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}这题就是传统的前缀和 + 哈希表,有个细节是为什么哈希表里只需记录第一次出现该前缀和时所对应的索引呢?因为体面给的是最长子数组长度,第一次出现的肯定最长
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public int maxSubArrayLen(int[] nums, int k) {
int len = nums.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prefix.length; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1];
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(prefix[i]-k)) {
res = Math.max(res, i - map.get(prefix[i]-k));
}
if (!map.containsKey(prefix[i])) {
map.put(prefix[i], i);
}
}
return res;
}
}这里和前面求 和为 k 的子数组个数 差不多,这里是维护同余的值与个数的 map,需要注意的是这里的在求余数时要考虑变成负数的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] nums, int k) {
int len = nums.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
count.put(0, 1);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prefix.length; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + nums[i-1];
// 可能是负数
int remainder = (prefix[i] % k) < 0 ? prefix[i] % k + k : prefix[i] % k;
if (count.containsKey(remainder)) {
res += count.get(remainder);
count.put(remainder, count.get(remainder) + 1);
} else {
count.put(remainder, 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}首先第一个转化点:以 8 为分界线,大于部分取 1,小于等于部分取 -1,以此问题就转化成了求和问题,只需要找子数组和满足大于 0 的最长数组即可
仍然利用前缀和 + 哈希表的方式,因为这里是求最长子数组且并没有给定求和值,所以求解方向就是求和满足最低要求使得数组范围仅可能大
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31class Solution {
private int[] prefix;
public int longestWPI(int[] hours) {
int len = hours.length;
prefix = new int[len + 1];
prefix[0] = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prefix.length; i++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + (hours[i-1] > 8 ? 1 : -1);
if (!map.containsKey(prefix[i])) {
map.put(prefix[i], i);
}
// 讨论 prefix[i] 的情况
if (prefix[i] > 0) {
res = Math.max(res, i);
} else {
// prefix[i] - prefix[j] > 0 且 j 要尽可能小
if (map.containsKey(prefix[i] - 1)) {
res = Math.max(res, i - map.get(prefix[i] - 1));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
差分数组
与前缀和类似,差分数组构建的目的是解决频繁对数组进行增减操作的效率问题
解决问题是构建一个差分数组,每个差分数组元素都是元素数对应位置与前一位置的差值,这已然可以想到对差值做增减将会反应的一整个范围原数组的值
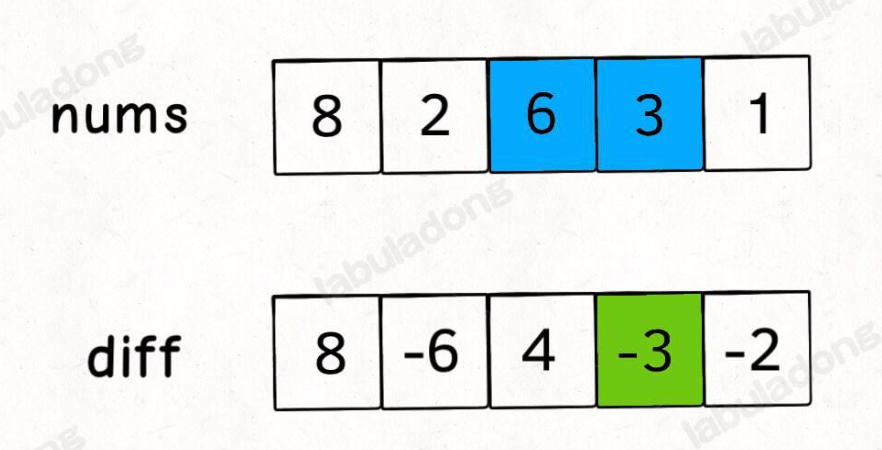
ex. 如果你想对区间
nums[i..j]的元素全部加 3,那么只需要让diff[i] += 3,然后再让diff[j+1] -= 3即可:
因此这里封装一个差分数组类:
1 | |
应用:
-
直接应用即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39class Solution {
private int[] diff;
private void inc(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
private int[] result() {
int[] result = new int[diff.length];
result[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
result[i] = result[i-1] + diff[i];
}
return result;
}
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) {
if (length == 0) {
return null;
}
diff = new int[length];
for (int[] update : updates) {
int i = update[0];
int j = update[1];
int val = update[2];
inc(i, j, val);
}
int[] res = result();
return res;
}
} -
本质上仍然是差分数组操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36class Solution {
private int[] diff;
private void inc(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
private int[] result() {
int[] res = new int[diff.length];
res[0] = diff[0];
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
res[i] = res[i-1] + diff[i];
}
return res;
}
public int[] corpFlightBookings(int[][] bookings, int n) {
diff = new int[n];
for (int[] booking : bookings) {
int i = booking[0];
int j = booking[1];
int val = booking[2];
inc(i-1, j-1, val);
}
int[] res = result();
return res;
}
} -
这里需要注意细节是下车的位置人数已经减少,所以这个区间增减区间应该是左闭右开的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40class Solution {
private int[] diff;
private void inc(int i, int j, int val) {
diff[i] += val;
if (j + 1 < diff.length) {
diff[j + 1] -= val;
}
}
public boolean carPooling(int[][] trips, int capacity) {
diff = new int[1000];
int[] seats = new int[1001];
for (int i = 0; i < seats.length; i++) {
seats[i] = capacity;
}
for (int[] trip : trips) {
int i = trip[1];
int j = trip[2] - 1;
int val = trip[0];
inc(i, j, val);
}
seats[0] = diff[0];
if (seats[0] > capacity) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 1; i < diff.length; i++) {
seats[i] = seats[i-1] + diff[i];
if (seats[i] > capacity) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
更抽象问题的套路框架:
1 | |
-
首先自变量是吃香蕉速度,因变量根据题意可知是吃完所需的时间。
最小速度 k表明要求左边界,但这里注意时间与速度之间呈反比关系1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29class Solution {
private int f(int[] piles, int x) {
// 因变量为按 x 速度吃香蕉所需时间
int hours = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < piles.length; i++) {
hours += piles[i] / x;
if (piles[i] % x != 0) {
hours++;
}
}
return hours;
}
public int minEatingSpeed(int[] piles, int h) {
int left = 1, right = 1000000000 + 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 单减函数
if (f(piles, mid) > h) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (f(piles, mid) <= h) {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
} -
二分部分好说,感觉天数那里不好算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36class Solution {
private int getDays(int[] weights, int x) {
int days = 0;
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) {
tmp += weights[i];
if (tmp > x) {
days++;
tmp = weights[i];
}
}
return days + 1;
}
public int shipWithinDays(int[] weights, int days) {
int left = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) {
left = Math.max(left, weights[i]);
}
int right = 25000000 + 1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (getDays(weights, mid) > days) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
} -
这里主要是思维的转换,仔细一想发现这道题其实本质上和前面运输船的问题是一样的。分成 m 个非空的连续子数组就是就是在 m 天运完所有货物;子数组对应着每天运输的货物量;而子数组和的最小值就是对应着最小载重
在二维矩阵中的应用:
-
这道题如果想用二分搜索,需要先转换为一维数组的索引形式
已知 二维数组的坐标
(i, j)可以映射成一维的index = i * n + j(二维数组的的行数m和列数n),那么 通过一维index反解出二维坐标i = index / n, j = index % n1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0, right = m * n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (get(matrix, mid) == target) {
return true;
} else if (get(matrix, mid) > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else if (get(matrix, mid) < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}
private int get(int[][] matrix, int index) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int i = index / n, j = index % n;
return matrix[i][j];
}
} -
这题巧妙方法在于我们可以将起点设置在右上角或者左下角,因为这样设置的话,朝两个方向走将要么增大要么减小,如此我们便可参考二分搜索的思路,根据与目标值作比较来决定是往元素变大的方向走还是往元素变小的方向走
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
while (i < m && j >= 0) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
j--;
} else if (matrix[i][j] < target) {
i++;
}
}
return false;
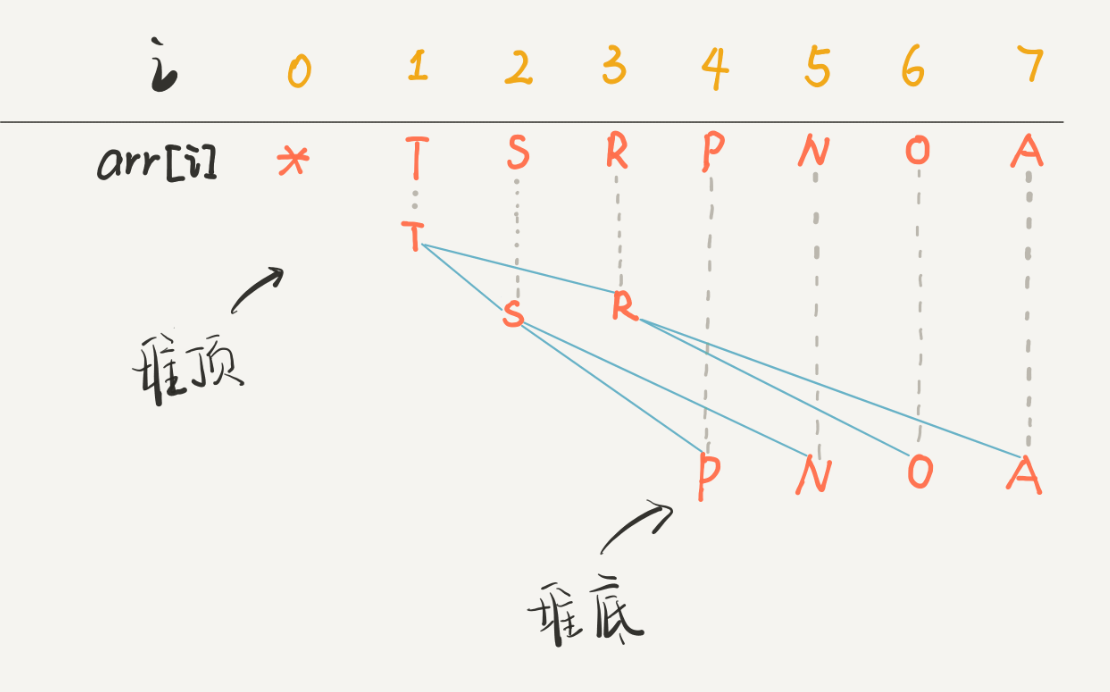
}「最接近元素」问题
-
这里首先用到二分查找的思路来定位目标元素,我们在这里定位左边界,因为根据题意
|a - x| == |b - x|且a < b是想让我们的下标尽量小;其次,利用「最长回文子串」的思想来从中心向两端扩张符合条件的元素直至已得到 K 个元素注意这里利用
LinkedList来保证结果的升序特性1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42class Solution {
public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) {
int p = findBinSearch(arr, x);
// 这里设置成开区间
int left = p - 1, right = p;
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while(right - left - 1 < k) {
if (left == -1) {
res.addLast(arr[right]);
right++;
} else if (right == arr.length) {
res.addFirst(arr[left]);
left--;
} else if (x - arr[left] > arr[right] - x) {
res.addLast(arr[right]);
right++;
} else {
res.addFirst(arr[left]);
left--;
}
}
return res;
}
// 升序
private int findBinSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0, right = arr.length;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
right = mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}「寻找峰值」
-
这里如何采用二分搜索的思想呢?也就是我们需要一个判定条件来移动我们的左右边界。我们可以根据探测值和周围的走势来判断:
如果走势下行(
nums[mid] > nums[mid+1]),说明mid本身就是峰值或其左侧有一个峰值,所以需要收缩右边界(right = mid);如果走势上行(
nums[mid] < nums[mid+1]),则说明mid右侧有一个峰值,需要收缩左边界(left = mid + 1)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
// 终止条件:left == right
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
// 左侧可能是高峰
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
} -
这个题就是寻找出来左右边界即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int l = leftBound(nums, target), r = rightBound(nums, target);
if (l == -1) {
return 0;
} else {
return r - l + 1;
}
}
private int leftBound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
if (left == nums.length) {
return -1;
}
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}
private int rightBound(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
if (left - 1 < 0) {
return -1;
}
return nums[left - 1] == target ? left - 1 : -1;
}
} -
传统做法:一次遍历,当然要考虑最后一个元素的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i != nums[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return i;
}如果用二分法的话,实际上是一次排出一般的数组元素,如何寻找判定条件?根据传统做法的思路,判断
nums[mid]和mid的关系即可:如果
nums[mid]和mid相等,则缺失的元素在右半边,如果nums[mid]和mid不相等,则缺失的元素在左半边考虑最后一个元素的情况,所以这里用搜索左边界的方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == mid) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
} -
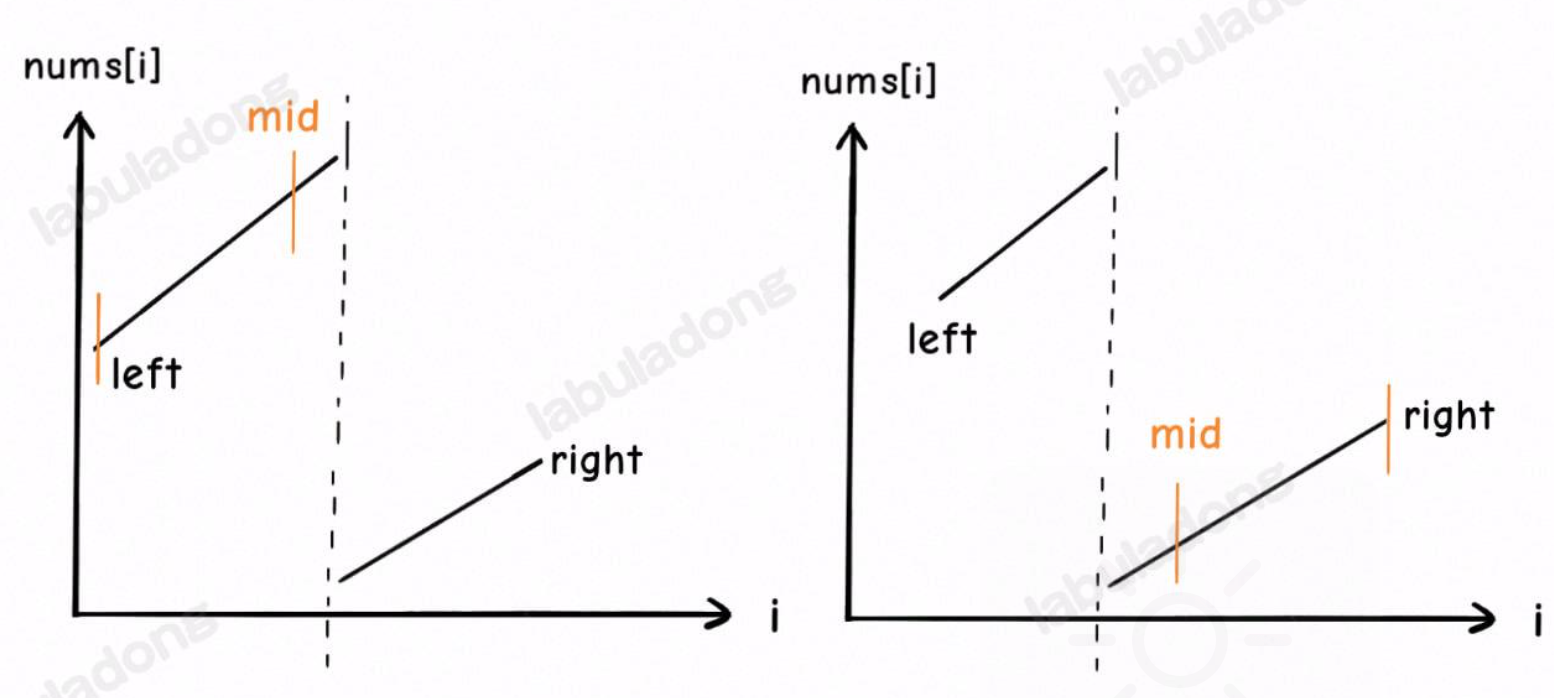
可以看到如图所示的情况,通过比较 mid 和左右边界的值即可判断当前 mid 落在左半部分还是右半部分;进一步再去判断 target 是落在了左半部分还是右半部分,来收缩左右边界。搜索方式和二分查找思路一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length -1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target == nums[mid]) {
return mid;
}
// 左半边
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else {
if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
} -
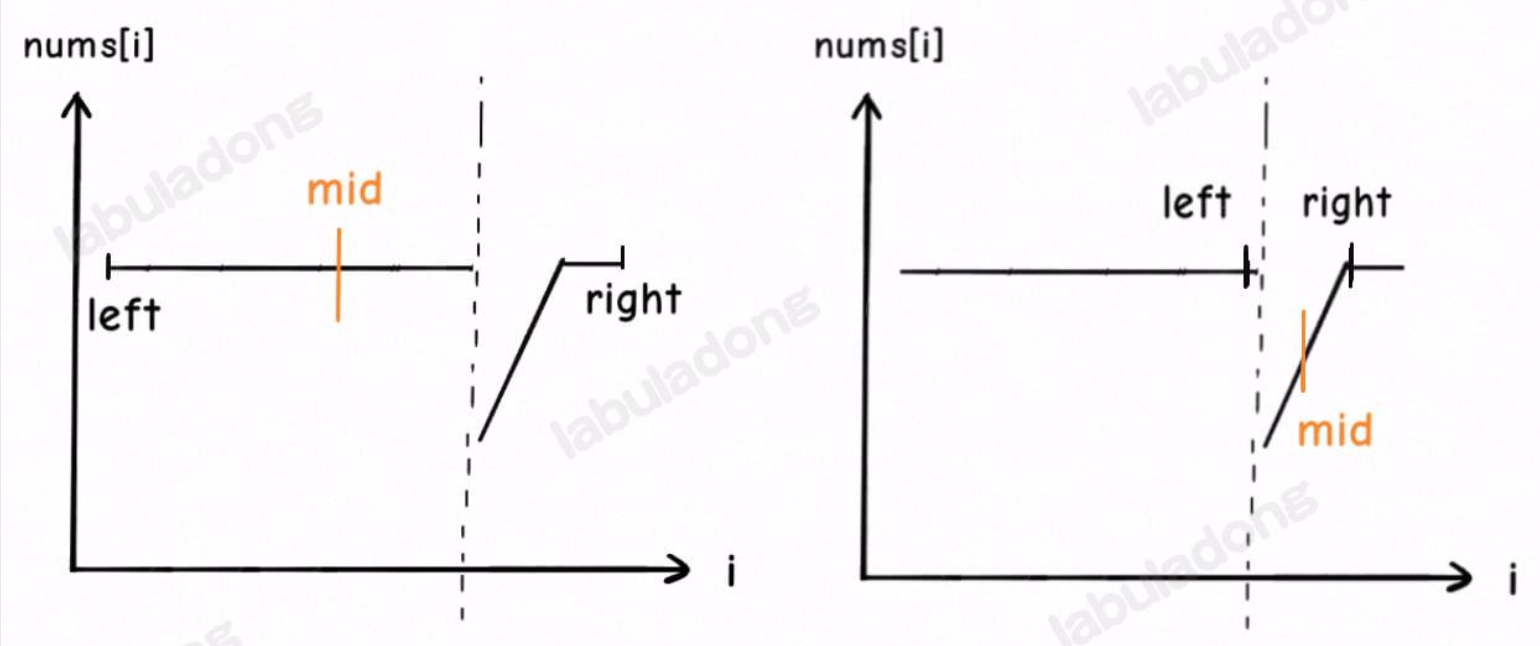
我们直接用上题的代码尝试,如下出错

原因即在于左右出现重复的部分,导致 mid 在判断左右区间时出错,而第二步就无法继续了。解决方法即我们先把重复元素去除,即开始时左右区间就向中间收缩,直至不存在重复元素为止(针对左半部分/ 右半部分而言)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length -1;
// 收缩左边界
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left+1]) {
left++;
}
// 收缩右边界
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right-1]) {
right--;
}
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target == nums[mid]) {
return true;
}
// 左半边
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else {
if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
滑动窗口算法技巧
算法框架:
1 | |
算法步骤:
1、我们在字符串
S中使用双指针中的左右指针技巧,初始化left = right = 0,把索引左闭右开区间[left, right)称为一个「窗口」。理论上你可以设计两端都开或者两端都闭的区间,但设计为左闭右开区间是最方便处理的。因为这样初始化
left = right = 0时区间[0, 0)中没有元素,但只要让right向右移动(扩大)一位,区间[0, 1)就包含一个元素0了。如果你设置为两端都开的区间,那么让right向右移动一位后开区间(0, 1)仍然没有元素;如果你设置为两端都闭的区间,那么初始区间[0, 0]就包含了一个元素。这两种情况都会给边界处理带来不必要的麻烦。2、我们先不断地增加
right指针扩大窗口[left, right),直到窗口中的字符串符合要求(包含了T中的所有字符)。3、此时,我们停止增加
right,转而不断增加left指针缩小窗口[left, right),直到窗口中的字符串不再符合要求(不包含T中的所有字符了)。同时,每次增加left,我们都要更新一轮结果。4、重复第 2 和第 3 步,直到
right到达字符串S的尽头。这个思路其实也不难,第 2 步相当于在寻找一个「可行解」,然后第 3 步在优化这个「可行解」,最终找到最优解,也就是最短的覆盖子串。左右指针轮流前进,窗口大小增增减减,窗口不断向右滑动,这就是「滑动窗口」这个名字的来历。
应用
-
这里注意需要一个初始 len 来排除未找到符合条件的子串的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
// 统计 t 中字符
HashMap<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
char c = t.charAt(i);
need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
// 记录最小覆盖子串的起始索引及长度
int start = 0, len = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 满足子串字符要求的个数
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
// c 是将移入窗口的字符
char c = s.charAt(right);
// 扩大窗口
right++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
if (need.containsKey(c)) {
window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
if (need.get(c).equals(window.get(c))) {
// 只有当 window[c] 和 need[c] 对应的出现次数一致时,才能满足条件,valid 才能 +1
valid++;
}
}
// 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
while (valid == need.size()) {
// 更新最优值
if (right - left < len) {
start = left;
len = right - left;
}
// d 是将移出窗口的字符
char d = s.charAt(left);
// 缩小窗口
left++;
// 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
if (need.containsKey(d)) {
if (need.get(d).equals(window.get(d))) {
// 只有当 window[d] 内的出现次数和 need[d] 相等时,才能 -1
valid--;
}
window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1);
}
}
}
// 返回最小覆盖子串
return len == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + len);
} -
这里实际上判定窗口收缩的条件就是窗口大小和子串大小一样的时候(因为子串是作为排列用,窗口中不能含有子串中没有的元素)
然后根据 valid 是否符合要求了来判断有没有找到符合条件的排列子串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
char c = s1.charAt(i);
need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0;
while (right < s2.length()) {
char c = s2.charAt(right);
right++;
if (need.containsKey(c)) {
window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
if (window.get(c).equals(need.get(c))) {
valid++;
}
}
// 收缩条件,窗口大小和子串长度一样时
if (right - left == s1.length()) {
if (valid == need.size()) {
return true;
}
char d = s2.charAt(left);
left++;
if (need.containsKey(d)) {
if (need.get(d).equals(window.get(d))) {
valid--;
}
window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1);
}
}
}
return false;
} -
直接套模板即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < p.length(); i++) {
char c = p.charAt(i);
need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, right = 0;
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
right++;
if (need.containsKey(c)) {
window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
if (window.get(c).equals(need.get(c))) {
valid++;
}
}
if (right - left == p.length()) {
if (valid == need.size()) {
res.add(left);
}
char d = s.charAt(left);
left++;
if (need.containsKey(d)) {
if (need.get(d).equals(window.get(d))) {
valid--;
}
window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1);
}
}
}
return res;
} -
这题只需要注意什么时候扩张窗口(遍历s时),什么时候收缩窗口(当 window 中记录的字符出现2次以上时),以及什么时候更新返回值(当收缩窗口结束的时候更新)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();
int res = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
right++;
// 记录
window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
// 收缩窗口
while (window.get(c) > 1) {
char d = s.charAt(left);
left++;
window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1);
}
// 收缩完后更新
res = Math.max(res, right-left);
}
return res;
} -
这里题意是让我们通过减去数组边缘的值来使得和为 x ,且尽可能使得操作数小。我们的目标可以转换为寻找最长子数组和为
num.sum - x1、当窗口内元素之和小于目标和
target时,扩大窗口,窗口内元素2、当窗口内元素之和大于目标和
target时,缩小窗口,空余出更多可替换次数。3、当窗口内元素之和等于目标和
target时,找到一个符合条件的子数组,我们想找的是最长的子数组长度PS:这里明确了元素值为大于 0. 的值,因此可以通过扩大和缩小窗口来实现和的增减;而如果值为负的话,则无法适用于该算法(应使用前缀和 + 哈希表的思路)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28public int minOperations(int[] nums, int x) {
int n = nums.length, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
}
int target = sum - x;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int window = 0;
int len = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (right < n) {
window += nums[right];
right++;
// shrink 这里注意左右边界
while (window > target && left < right) {
window -= nums[left];
left++;
}
if (window == target) {
// update
len = Math.max(len, right-left);
}
}
return len == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? -1 : n - len;
} -
这里滑动思路和前面一样,但是在更新记录符合条件的窗口值时要考虑子集的情况
比方说 left = 1, right = 4 划定了 [1, 2, 3] 这个窗口(right 是开区间)
但不止 [left..right] 是合法的子数组,[left+1..right], [left+2..right] 等都是合法子数组
所以我们需要把 [3], [2,3], [1,2,3] 这 right - left 个子数组都加上PS: 对于 [1] [2] 和 [1,2] 在上一轮更新时已被记录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public int numSubarrayProductLessThanK(int[] nums, int k) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
int window = 1;
int count = 0;
while (right < nums.length) {
window *= nums[right];
right++;
while (window >= k && left < right) {
window /= nums[left];
left++;
}
// 这里必然符合条件
count += right - left;
}
return count;
} -
还是之前的三个问题,能回答出来就能写
1、当可替换次数大于等于 0 时,扩大窗口,让进入窗口的 0 都变成 1,使得连续的 1 的长度尽可能大。
2、当可替换次数小于 0 时,缩小窗口,空余出可替换次数,以便继续扩大窗口。
3、只要可替换次数大于等于 0,窗口中的元素都会被替换成 1,也就是连续为 1 的子数组,我们想求的就是最大窗口长度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public int longestOnes(int[] nums, int k) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
int windowOneCount = 0;
int len = 0;
while (right < nums.length) {
if (nums[right] == 1) {
windowOneCount++;
}
right++;
// 当窗口内 0 的数目超过 k 个后
while (right - left - windowOneCount > k) {
if (nums[left] == 1) {
windowOneCount--;
}
left++;
}
// 这时一定是符合条件的
len = Math.max(len, right - left);
}
return len;
} -
这道题和上一题的区别在于需要自己选择替换的字符,所以这里借助一下统计数组,每次替换都是用的字符统计数量最大的。
注意,在窗口收缩的时候,要保证最大的重复子串长度不变 windowSize (可以用 k 替换的,所以这里只变化 left)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public int characterReplacement(String s, int k) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
int windowSize = 0;
int[] count = new int[26];
int len = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
right++;
count[c - 'A']++;
windowSize = Math.max(windowSize, count[c - 'A']);
// shrink
while (right - left - windowSize > k) {
char d = s.charAt(left);
count[d - 'A']--;
left++;
}
len = Math.max(len, right - left);
}
return len;
} -
这道题可以维护一个窗口大小为 k 的 HashSet,当添加一个新元素的时候只要判断是否包含就能说明肯定满足题意。另外,当窗口大小大于 k 时缩小窗口,小于 k 时就增大窗口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
HashSet<Integer> window = new HashSet<>();
while (right < nums.length) {
if (window.contains(nums[right])) {
return true;
}
window.add(nums[right]);
right++;
if (right - left > k) {
window.remove(nums[left]);
left++;
}
}
return false;
} -
TODO 这道题在判断元素之差时需要借助二叉搜索树
-
这道题的关键在于如何自己构造一个阈值来判断什么时候增大窗口,什么时候缩小窗口;至少有 K 个重复字符,题意并未说明字符种类的限制,那么我们可以遍历 1-26 种类的字符对应的满足条件的最长子串长度,其中最大值一定就是题解。这样每一轮循环设置一个种类数量限制,小于该限制时窗口增大,大于时窗口减小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61class Solution {
public int longestSubstring(String s, int k) {
int len = 0;
// 穷举遍历所有字符种类下对应的最长子串长度
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
len = Math.max(len, logestKLetterSubstr(s, k, i));
}
return len;
}
private int logestKLetterSubstr(String s, int k, int i) {
// 返回长度
int res = 0;
int left = 0, right = 0;
// 统计字符次数
int[] count = new int[26];
// 窗口中出现的字符个数
int windowCountSize = 0;
// 窗口中达标的字符个数,即出现次数大于等于 k 的个数
int windowValidSize = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char d = s.charAt(right);
if (count[d - 'a'] == 0) {
windowCountSize++;
}
count[d - 'a']++;
if (count[d - 'a'] == k) {
windowValidSize++;
}
right++;
// 当字符种类大于 i 时,缩小窗口
// 这里应该用 while 而不是 if ,因为移除的元素不一定会是的 count 减小
while (windowCountSize > i) {
char p = s.charAt(left);
if (count[p - 'a'] == k) {
windowValidSize--;
}
count[p - 'a']--;
if (count[p - 'a'] == 0) {
windowCountSize--;
}
left++;
}
// 更新参数
if (windowValidSize == i) {
res = Math.max(res, right - left);
}
}
return res;
}
}